a) Withstand voltage test:
The basic working principle is: the leakage current generated by the instrument under test in the withstand voltage tester output high voltage and the preset judgment current comparison, if the detected leakage current is less than the preset value, the instrument passes the test, when the detected leakage current is greater than the judgment current, the test voltage is cut off instantaneously and sound and light alarm is issued, so as to determine the pressure strength of the measured piece.
For the first test loop grounding test principle, refer to Figure 1:
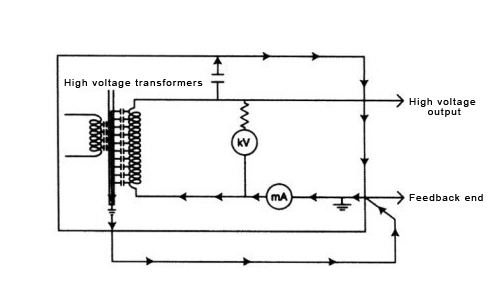
Withstand voltage tester is mainly composed of AC (direct) high voltage power supply, timing controller, detection circuit, indication circuit and alarm circuit, the basic working principle is: the leakage current generated by the instrument under test under the high voltage output of the withstand voltage tester and the preset judgment current comparison, if the detected leakage current is less than the preset value, the instrument passes the test, when the detected leakage current is greater than the judgment current, the test voltage is instantaneously cut off and sound and light alarm, so as to determine the withstand voltage strength of the measured piece.
b) Insulation resistance:
We know that the voltage of the insulation resistance test is generally DC 500V or 1000V, which is equivalent to testing a DC withstand voltage test, the instrument measures a current value under this voltage, and then calculates through the internal line, amplifies this current, and finally passes Ohm's law: R = U/I, where U is the test of 500V or 1000V, and I is the leakage current at this voltage, according to the withstand voltage test experience we can understand that this current is very small, Typically less than 1μA.
It can be seen from the above that the principle of insulation resistance test is exactly the same as the withstand voltage test, but it is another expression of Ohm's law, the withstand voltage test uses leakage current to express the insulation performance of the measured object, and the insulation resistance is to use resistance.
2) The purpose of the withstand voltage test:
The withstand voltage test is a non-destructive test, which is used to detect whether the insulation ability of the product is qualified under the frequent transient high voltage. It applies a high voltage to the device under test for a certain period of time to ensure that the insulation of the equipment is strong enough. Another reason for this test is that it can also detect some defects of the instrument, such as insufficient creepage distance and insufficient clearance during manufacturing.
3) Withstand voltage test voltage:
There is a general rule test voltage = supply voltage× 2+1000V.
For example, if the power supply voltage of the test product is 220V, the test voltage = 220V × 2+1000V = 1480V.
The typical withstand voltage test time is one minute. Due to the extensive electrical resistance tests of products on the production line, the test time is often reduced to only a few seconds. There is a typical practical principle, when the test time drops to only 1~2 seconds, the test voltage must be increased by 10~20% to ensure the reliability of insulation during short-term testing.
4) Alarm current
The alarm current setting should be determined according to different products. The best way is to test a batch of samples for leakage current beforehand, get an average, and then determine a value slightly above this average as the set current. Since there is inevitably a certain leakage current in the instrument under test, it should be ensured that the set alarm current is large enough to avoid being triggered by the leakage current, and it should be small enough to avoid letting go of unqualified samples. In some cases, it is also possible to determine whether the sample is in contact with the output of the withstand voltage tester by setting a so-called lower alarm current.
5) Selection of AC and DC test
Test voltage, most safety standards allow the use of AC or DC voltage in withstand voltage testing. If AC test voltage is used, the insulator to be measured is subjected to maximum pressure when the voltage peak is reached, whether it is a positive or negative polarity peak. Therefore, if you decide to use DC voltage testing, you must ensure that the DC test voltage is √ 2 times the AC test voltage so that the DC voltage can be equal to the AC voltage peak. For example: 1500V AC voltage, for DC voltage to produce the same amount of electrical stress must be 1500 × 1.414 i.e. 2121V DC voltage.
One of the advantages of using DC test voltage is that in DC mode, the current flowing through the withstand voltage tester alarm current measurement device is the actual current flowing through the sample. Another advantage of using DC testing is that the voltage can be applied gradually. By monitoring the current flowing through the sample as the voltage increases, the operator can detect breakdown before it occurs. It should be noted that when using a DC withstand voltage tester, the sample must be discharged after the test is completed due to the capacitance charging in the circuit. In fact, regardless of the test voltage and its product characteristics, it is good to discharge the product before operating it.
The disadvantage of DC withstand voltage test is that it can only apply the test voltage in one direction, and can not apply electrical stress on both polarities like AC testing, and most electronic products work under AC power. In addition, DC testing is more expensive than AC testing because DC test voltage is difficult to generate.
The advantage of AC withstand voltage test is that it can detect all voltage polarities, which is closer to the actual practical situation. In addition, since the AC voltage does not charge the capacitor, in most cases, a stable current value can be obtained by directly outputting the corresponding voltage without a gradual boost. Also, after the AC test is completed, there is no need for sample discharge.
The disadvantage of AC withstand voltage testing is that if there is a large Y capacitance in the line under test, in some cases, the AC test will be misjudged. Most safety standards allow users not to connect a Y-capacitor before testing, or to use DC testing instead. The DC withstand voltage test does not misjudge when the voltage is applied to the Y capacitor, because the capacitor will not allow any current to pass through at this time.
The withstand voltage is actually to verify the clearance, for the air the clearance is enough, the insulation must not break down, the above are all IEC said. Insulation under some fault conditions is also considered. The problem of DC AC, the standard says, if there is a cross-border Y capacitor, DC is recommended.


 Nina She
Nina She